Protecting Digital Twins: Securing Virtual Representations of Physical Assets
- bakhshishsingh
- Aug 12, 2024
- 5 min read
Updated: Feb 3, 2025
Introduction:
Imagine a world where every physical object has a virtual doppelganger, a digital replica that mirrors its real-world counterpart in real-time. This isn't science fiction – it's the world of digital twins, and it's already here. Digital twins are virtual representations of physical objects or systems that use real-time data to mirror the state of their physical counterparts. From jet engines to entire cities, digital twins are revolutionizing how we interact with and understand the physical world. But as with any technological advancement, this innovation brings new challenges – particularly in the realm of security.
Applications of Digital Twins:
The versatility of digital twins is astounding. In manufacturing, they're the backbone of Industry 4.0, allowing companies to simulate and optimize production processes before implementation. Siemens, for instance, uses digital twins to improve product development, reducing time-to-market by up to 50% [Source: Siemens].
In urban planning, digital twins are transforming cities. Singapore's "Virtual Singapore" project is a prime example, creating a dynamic 3D city model used for everything from urban planning to disaster response simulations [Source: National Research Foundation, Singapore].
Healthcare is another frontier for digital twins. Researchers are developing patient-specific digital twins to personalize treatments and predict health outcomes. The Living Heart Project by Dassault Systèmes is pioneering this approach with a realistic 3D heart model [Source: Dassault Systèmes].
In aerospace, companies like Boeing use digital twins to monitor aircraft performance and predict maintenance needs, potentially saving millions in unexpected downtime [Source: Boeing].
The Security Imperative for Digital Twins:
With great power comes great responsibility – and great risk. Digital twins, by their nature, are treasure troves of sensitive data. A compromised digital twin could lead to leaked trade secrets, manipulated urban infrastructure, or even life-threatening situations in healthcare applications.
Imagine a hacker gaining control of a digital twin representing a power plant. They could potentially manipulate the virtual model to send false data to operators, leading to real-world disruptions or damage. The interconnected nature of digital twins and physical assets means that a breach in the virtual world can have tangible, and potentially catastrophic, consequences in the real world.
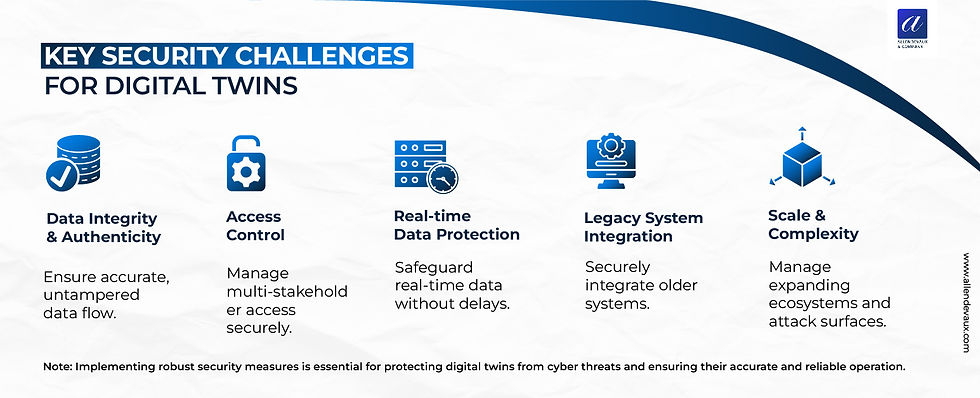
Key Security Challenges:
Securing digital twins is no small feat. Here are some of the key challenges:
1. Data Integrity and Authenticity: Ensuring that the data feeding the digital twin is accurate and hasn't been tampered with is crucial.
2. Access Control: With multiple stakeholders often involved, managing who has access to what parts of the digital twin is complex but vital.
3. Real-time Data Protection: Digital twins often operate on real-time data, requiring security measures that don't impede this immediacy.
4. Legacy System Integration: Many digital twins need to integrate with older systems that may not have been designed with modern security in mind.
5. Scale and Complexity: As digital twin ecosystems grow, so does the attack surface, making comprehensive security increasingly challenging.
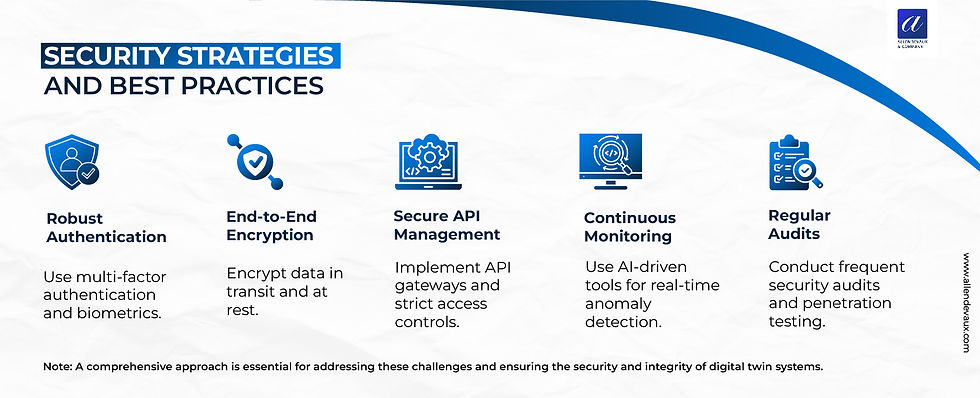
Security Strategies and Best Practices:
To address these challenges, organizations need a multi-faceted approach:
1. Robust Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication and consider biometric measures for critical systems.
2. End-to-End Encryption: Use strong encryption for data both in transit and at rest to protect against interception and theft.
3. Secure API Management: As digital twins often rely on APIs for data exchange, securing these interfaces is crucial. Use API gateways and implement strict access controls.
4. Continuous Monitoring: Employ AI-driven monitoring tools to detect anomalies in real-time and alert to potential security breaches.
5. Regular Audits: Conduct frequent security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Emerging Technologies for Digital Twin Security:
As digital twins evolve, so too must our security measures. Several
emerging technologies show promise:
1. Blockchain: Its immutable nature makes blockchain an excellent
tool for maintaining the integrity of digital twin data. IBM's
Blockchain Platform is being explored for this purpose [Source: IBM].
2. AI and Machine Learning: These technologies can help detect
anomalies and potential security threats faster than human
operators. Companies like Darktrace are pioneering AI-driven
cybersecurity solutions [Source: Darktrace].
3. Edge Computing: By processing data closer to its source, edge
computing can reduce the attack surface and improve response
times. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated
data will be processed at the edge [Source: Gartner].
4. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: As quantum computing
threatens to break current encryption methods, companies like IBM
and Microsoft are working on quantum-resistant algorithms to
future-proof data protection [Source: IBM Research].
Regulatory Considerations:
The regulatory landscape for digital twins is still evolving, but existing data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA already have significant implications. Organizations must ensure their digital twin implementations comply with data privacy regulations, which can be challenging given the vast amounts of data involved.
Industry-specific regulations also come into play. For instance, digital twins in healthcare must comply with HIPAA in the US, while those in finance need to adhere to regulations like PSD2 in Europe.
Compliance isn't just about avoiding fines – it's about building trust with customers and partners. Organizations should view regulatory compliance as an opportunity to strengthen their security posture and demonstrate their commitment to data protection.
Case Studies:
Let's look at a couple of real-world examples:
1. GE's Digital Twin Success: GE Aviation uses digital twins to monitor and predict the maintenance needs of aircraft engines. By securely collecting and analyzing data from sensors on actual engines, they've been able to improve engine performance and reduce unplanned downtime. Their robust security measures, including end-to-end encryption and strict access controls, have been key to maintaining customer trust [Source: GE Digital].
2. Learning from Near-Misses: While not specifically a digital twin case, the 2021 attempt to poison a Florida city's water supply through a remote access system highlights the potential dangers of unsecured digital systems controlling physical infrastructure. This incident underscores the importance of robust security measures for digital twins, especially those controlling critical systems [Source: CNN].
Future Outlook:
The future of digital twins is bright, but it's intertwined with advancements in security. We can expect to see more sophisticated AI-driven security measures, increased use of edge computing for improved data protection, and potentially the integration of quantum computing for unbreakable encryption.
New use cases will emerge, bringing new security challenges. For instance, as digital twins start to be used more in personal health monitoring or autonomous vehicles, the security implications will become even more critical.
Conclusion:
Digital twins represent a paradigm shift in how we interact with and understand the physical world. They offer unprecedented insights and efficiencies across industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. However, their full potential can only be realized if we can trust in their security.
As we've seen, protecting digital twins is a complex challenge that requires a multi-faceted approach. It's not just about implementing the latest security technologies – though that's certainly part of it. It's about fostering a security-first mindset, staying ahead of emerging threats, and understanding the unique vulnerabilities that come with bridging the physical and digital worlds.
For organizations leveraging or considering digital twin technology, the message is clear: security cannot be an afterthought. It must be baked into every aspect of your digital twin strategy from the outset. By doing so, you're not just protecting data – you're safeguarding the promise of this transformative technology.
The future is digital, and increasingly, it's mirrored. Let's ensure it's secure.





Comments